Standard Suite
Extensions & Plugins
Power Suite
Apps & Tools

Whether you are creating a simple paint program or a complex application for vector graphics animation, this powerful rasterizing library is for you. Using a very simple set of instructions, create output primitives with smooth, anti-aliased edges in no time!
30-Day Evaluation
(Windows, Mac, Linux)

Release 9.0
See What's New
D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer represents the foundation of D-Type scalable rendering technology. This powerful and portable C/C++ library can quickly, easily and reliably convert arbitrary vector shapes (outlines) to high quality anti-aliased bitmaps, while supporting any output size, resolution, device and CPU architecture. D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer has been extensively optimized for speed and by default makes no use of the floating-point math. For the highest level of performance, D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer can utilize multiple worker threads to render concurrently. All these unique features, combined with many other state-of-the-art algorithms and advanced code, make D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer the world's fastest software rasterizer.
D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer allows developers to easily construct and render shapes of any type, size or complexity. Two complementary methods are available:
To easily draw common 2D primitives such as lines, Bézier and B-spline curves, arcs, circles, ellipses, rectangles, polygons etc. developers can utilize a helper library of common 2D primitives. These primitives can be drawn solid or dashed using a custom thickness, while their ends can be flat, rounded (inside or outside) or marked using special symbols (dots, arrows etc). An affine transformation matrix can be applied to any 2D primitive, so the final shape can be drawn stretched, skewed and/or rotated.
To draw a completely arbitrary shape, developers can define its outline using straight and/or curved segments and pass it to D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer for direct rendering. It's super fast and easy.
Regardless of the shape construction method, D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer produces exactly the same output, down to the pixel, on any platform your application targets — Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android or perhaps your own custom embedded system. As with all other D-Type rendering engines, developers can draw to their own device independent memory surfaces, which includes a plethora of formats such as 8-bpp grayscale, 16-bpp, 24-bpp RGB and various 32-bpp RGBA formats and, optionally, apply various styles (color, transparency, shadows, blurring, embossing effects, patterns etc.) during the rasterization process.
D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer is known for its small footprint, unmatched speed, advanced architecture and crisp, smooth, high-quality output. It should come as no surprise that both D-Type Font Engine and D-Type PowerDoc Engine internally rely on D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer to render fonts and other complex scalable 2D objects.
| Grayscale Levels |
|
|---|---|
| Coordinates |
|
| Filling Method |
|
| Advanced Features |
|
| Availability |
|
To see D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer in action, compare the following two illustrations:
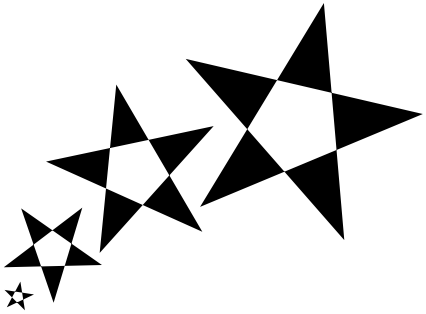

Although both illustrations represent two identical groups of objects rendered at the same resolution, the difference in quality is obvious. Compared to ordinary black & white rasterizers, D-Type Grayscale Rasterizer increases the number of addressable points on the screen significantly. The result is absolutely superior quality and always smooth edges.
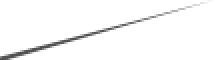
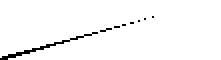
Thin lines and skinny polygons are very difficult to render properly at low resolutions. But with D-Type's dropout prevention you always get the best possible results (left). See the same object rendered by an ordinary rasterizer that lacks support for dropout prevention (right).

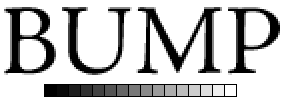
Certain rasterizers can only render using a limited number of gray levels. For example, Adobe Photoshop uses only 16 levels. Compare that with D-Type's 256 gray levels. The difference in quality is quite obvious, especially when rendering small text and other objects with fine detail.
Click the thumbnail to see a larger version of the image.